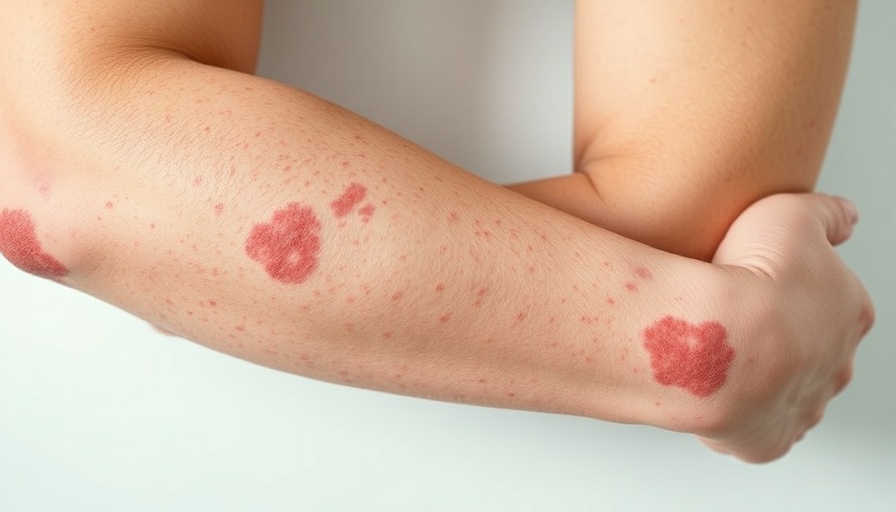
Understanding the Link Between Diabetes, Kidney Disease, and Psoriasis
Recent research reveals a troubling connection between diabetes, kidney disease, and an increased risk of psoriasis. Patients suffering from kidney disease while managing diabetes face higher chances of developing this chronic skin condition. This intersection of diseases underscores the importance of understanding how multiple health issues can compound and exacerbate overall patient well-being.
The Rising Prevalence of Psoriasis in Diabetic Patients
Psoriasis, an autoimmune disorder that leads to rapid skin cell production resulting in scaly patches, has been linked with several systemic diseases, including chronic kidney disease (CKD). Studies indicate that patients with psoriasis, particularly moderate to severe cases, experience a significant increase in the risk of developing both CKD and end-stage renal disease (ESRD). This correlation is particularly concerning for diabetes patients, as those with existing kidney problems are already vulnerable to a range of diseases and complications.
Causative Factors: Inflammation and Immune Responses
The exact mechanisms linking these conditions remain complex and elusive. Autoimmune diseases like psoriasis trigger systemic inflammation, which can adversely affect kidney function. For instance, the presence of inflammatory markers in the bloodstream, such as those from psoriatic conditions, can lead to renal inflammation, further complicating kidney health. It has been theorized that treatments targeting these inflammatory processes might hold potential for protecting renal function in psoriasis patients.
Recent Findings: The Study Insights
A systematic review examining the prevalence of CKD and ESRD in psoriasis patients suggests a higher risk factor for those with severe psoriasis. In fact, research presents compelling evidence that patients with severe psoriasis are over twice as likely to develop CKD compared to those without the condition, reinforcing the need for comprehensive monitoring in these patients. This connection is particularly salient for individuals managing diabetes, where kidney health is already a critical concern.
The Importance of Monitoring and Early Intervention
Continuous monitoring and early intervention strategies can drastically improve outcomes for patients at risk. Routine screenings, including blood and urine tests, can be lifesaving. This is essential for diabetic patients with psoriasis as early detection of any decline in kidney function allows for timely therapeutic modifications, potentially helping to avert severe complications.
Healthcare’s Role in Managing Multiple Conditions
Healthcare providers must adopt a holistic view of patient care, especially for those grappling with multiple chronic conditions. The intersection of diabetes, kidney disease, and psoriasis necessitates an interdisciplinary approach, involving dermatologists, nephrologists, and endocrinologists to optimize patients' health outcomes. Educating patients about the implications of their conditions can empower them to be active participants in their healthcare management.
Moving Forward: Knowledge is Power
Understanding the interconnectedness of these diseases not only aids in better management strategies but can also open doors for future research. Increased awareness of the relationship between psoriasis and kidney disease can inspire further studies aimed at elucidating the underlying mechanisms, effectively guiding treatment protocols and improving patient quality of life.
If you manage diabetes or have been diagnosed with psoriasis, it’s crucial to speak with your healthcare provider about the risks associated with kidney disease and consider regular screenings. Prevention starts with knowledge, and early intervention can significantly affect long-term health outcomes.
 Add Row
Add Row  Add
Add 



Write A Comment