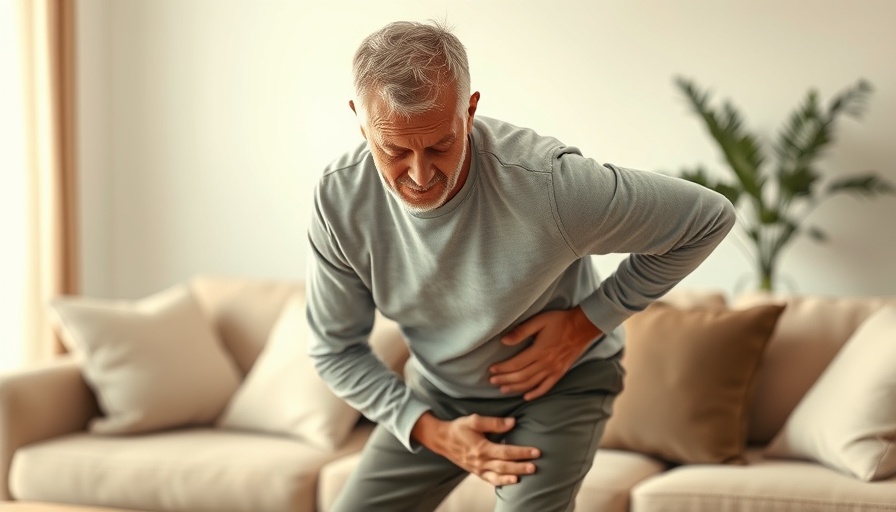

Understanding Early Knee Damage: A Surprising Reality for Many
For many young adults in their 30s, the bustling days of sports and active living seem like distant memories. However, a recent study sheds light on a concerning reality: many individuals may be experiencing early knee damage without even knowing it. Traditionally, knee osteoarthritis and joint deterioration have been associated with aging, yet MRI scans reveal that a significant portion of young adults already show signs of this condition.
The Science Behind the Study
The groundbreaking research is documented in the journal Osteoarthritis and Cartilage, which examines MRI findings from a diverse cohort of 288 participants averaging 33.7 years of age. The study revealed that nearly two-thirds exhibited early cartilage damage or signs of bone overgrowth, particularly at the patellofemoral joint where the kneecap meets the thigh bone. Shockingly, many of these individuals reported no knee pain, indicating that silent degeneration has become an alarming trend.
Surveying the Symptoms: What Does the Data Say?
Among the subjects scanned, a staggering 56.2% showed cartilage deterioration, while a further 25.3% exhibited bone irregularities. Yet, the telltale absence of pain is what complicates the landscape: how can one be so damaged yet remain blissfully unaware? The non-clinical symptoms often lead to delayed diagnoses, prompting the need for greater awareness in our youth.
Contributors to Knee Damage: Analyzing Risk Factors
What factors contribute to this trend of early knee damage? Researchers highlighted obesity and high body mass index (BMI) as significant influencers. In a society where sedentary lifestyles proliferate and physical activity is often minimal, the toll on joint health is becoming increasingly evident. Additionally, family history plays a critical role. Those with a lineage of knee-related ailments find themselves at greater risk of facing similar challenges.
The Social Implication of Silent Degeneration: What This Means for Society
This trend holds serious implications not just for individuals but society as a whole. The prevalence of silent knee damage risks leading to increased healthcare costs and diminished quality of life for a sizeable demographic. As young adults are often the backbone of a productive society, facing premature joint issues could result in increased absenteeism and lower productivity levels.
Looking Ahead: The Need for Proactive Measures
What does the future hold for knee health among the young population? A proactive approach is essential. Regular check-ups and awareness of body signals play a crucial role in early detection. Furthermore, promoting physical activity and healthier lifestyle choices through community programs could alleviate some of these issues. Education on how to maintain joint health, particularly amid rising obesity rates, is vital, as is encouraging individuals to seek medical advice at the first sign of discomfort.
Advice for Young Adults: Step Towards Prevention
Young adults should take precautions to ensure they do not become another statistic in this unfolding reality. Engaging in regular physical activity can help maintain healthy joints, while monitoring diet choices can combat obesity. Additionally, gradual conditioning through no-impact exercises, such as swimming and cycling, can build strength without placing undue stress on knees. Understanding one’s family history and consulting healthcare professionals when necessary can also play a significant role in prevention.
Final Thoughts: Why This Matters
The findings from this study highlight a growing concern that resonates with many. The silent degradation of knee health in young adults calls for immediate attention, emphasizing the importance of preventive care and lifestyle adjustments. If we can foster a culture of awareness and proactive health management, we may reverse, or at least slow, the tide of premature knee damage.
This topic has widespread relevance, particularly among younger populations increasingly affected by these silent injuries. Take action now to ensure your joints remain healthy well into the future.
 Add Row
Add Row  Add
Add 



Write A Comment