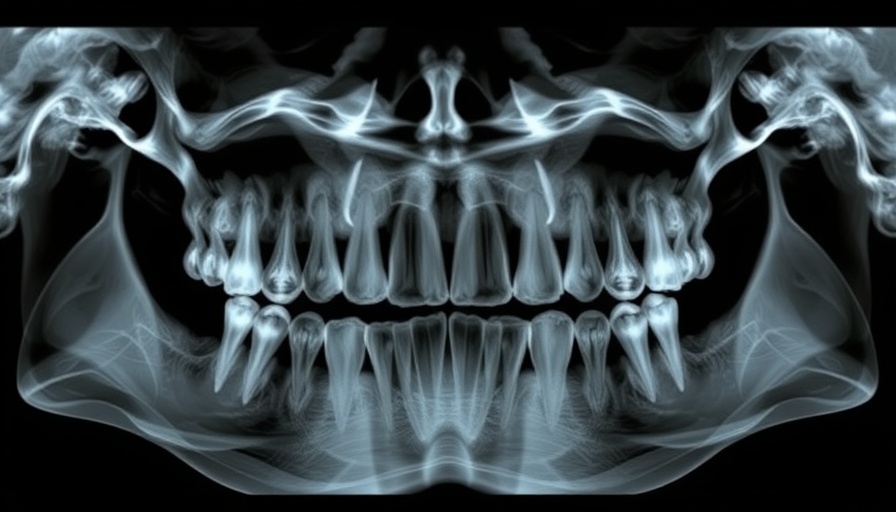
Understanding Widespread Dental Pulp Calcification
In the realm of oral health, dental pulp calcification is often an overlooked yet significant phenomenon. Recently, a case involving a patient with Systemic Lupus Erythematosus (SLE) receiving long-term steroid therapy has shed light on the impacts this condition can have on dental structures. The calcification found within the pulp tissues of teeth poses questions not only about the direct health implications for patients but also about the broader impact of long-term steroid treatments.
The Link Between SLE and Dental Health
Systemic Lupus Erythematosus, an autoimmune condition, has far-reaching effects on various organ systems, including oral health. Patients often undergo extensive treatments, including long-term corticosteroid therapy, which, unfortunately, can lead to various dental complications. The case at hand highlights a crucial aspect of this relationship—the need for dental practitioners to be aware of potential pulp calcification in SLE patients. Research indicates that glucocorticoids can influence the metabolic processes in dental tissues, leading to conditions such as pulp calcification. Understanding these implications is vital for dentists who treat patients with SLE.
What Does Pulp Calcification Mean?
Pulp calcification refers to the deposition of calcified materials within the pulp tissue of teeth, a condition that can hinder dental health significantly. This calcification can lead to various symptoms, including pain, sensitivity, and even the risk of tooth loss if not addressed timely. For patients on long-term steroid therapy, such as those with SLE, recognizing the signs of pulp calcification can be crucial in managing overall oral health and ensuring timely interventions. Additionally, studies show an increased prevalence of dental anomalies and pulp changes in patients with SLE, further emphasizing the need for vigilant monitoring.
Impact of Long-Term Steroid Therapy on Oral Health
Long-term steroid therapy carries various risks, including osteoporosis, increased infection rates, and metabolic changes that can also affect dental health. These risks are particularly pertinent for SLE patients who may already be experiencing compromised immune function. Dental care providers play a key role in managing these risks by conducting regular examinations and proactively addressing any abnormalities. Steroid-induced changes can prompt a reevaluation of treatment plans, ensuring that both systemic and dental health are prioritized.
Actionable Insights for Dental Practitioners
For dental professionals, understanding the intricate relationship between systemic conditions like SLE and dental complications is paramount. Here are some actionable insights:
- **Regular Screening**: Patients on long-term steroid therapy should be regularly screened for dental pulp calcifications and other related complications.
- **Interdisciplinary Collaboration**: Dental practitioners should work closely with rheumatologists and other healthcare providers managing SLE patients to ensure comprehensive care.
- **Patient Education**: Teaching patients about the potential dental complications related to their treatment can empower them to seek timely care.
Future Implications and Research Directions
This case also opens the door for further research in the area of dental implications in autoimmune disorders. Understanding how systemic disease management impacts oral health could lead to improved treatment protocols. Future studies could focus on the mechanisms behind pulp calcification in SLE patients and explore preventative measures that can be implemented within dental practices.
By raising awareness of these dental health implications, the dental community can better serve patients with complex medical histories, ultimately enhancing their quality of life and health outcomes.
 Add Row
Add Row  Add
Add 




Write A Comment