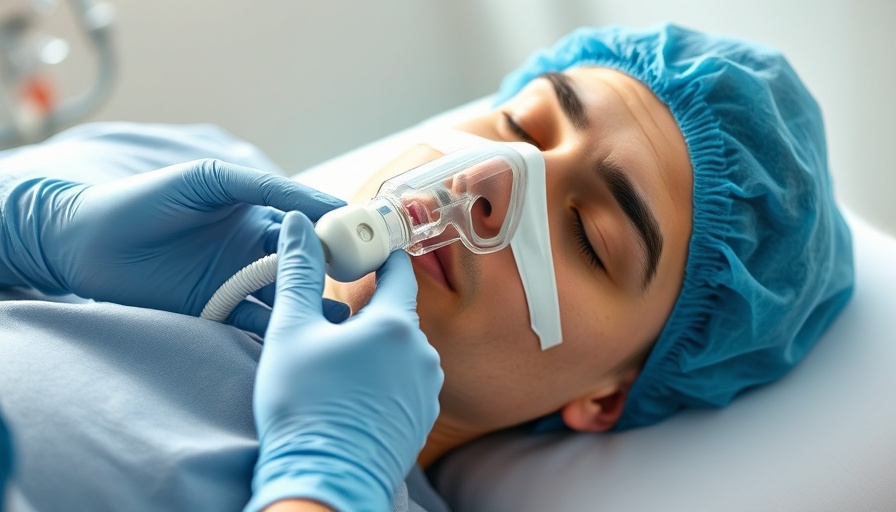
Addressing the Climate Crisis: The Role of Anesthesia
As the world grapples with climate change, the healthcare sector is stepping up to address its environmental impact. The recent research into the removal of desflurane vaporisers in anesthesia departments offers a glimpse into how thoughtful changes in practice can significantly reduce greenhouse gas emissions. Desflurane is known to have a global warming potential 2,500 times greater than carbon dioxide, making its removal not only a wise clinical decision but a moral imperative for hospitals.
Climate Impact of Inhaled Anesthetics
Studies from organizations such as the American Society of Anesthesiologists reveal that inhaled anesthetics—especially desflurane—contribute disproportionately to global greenhouse gas emissions. Representing about 3% of the UK National Health Service's (NHS) carbon footprint, the switch away from desflurane can lead to a reduction of around 40 kilotonnes of carbon a year. Such figures illustrate the critical intersection between healthcare and climate responsibility.
Historical Context: The Evolution of Anesthesia
Since its inception in 1846, anesthesia has been a lifesaving tool in medicine, enabling countless surgical procedures. However, as technology and practices evolve, so must our awareness of their environmental consequences. The decommissioning of desflurane across NHS hospitals by early 2024, with exceptions for rare clinical circumstances, indicates an evolving consciousness within the medical community regarding sustainable practices.
Examining Successful Strategies in Emission Reduction
The results from various NHS trusts demonstrate that proactive steps, such as staff training and modifying protocols, can drastically reduce emissions. Trusts like Norfolk and Norwich are leading the way, already eliminating desflurane in their practices. Training ensures that staff are well-equipped to use more sustainable alternatives, reinforcing a culture of responsibility and ecological awareness.
Understanding Emission Intensive Practices
The high greenhouse gas emissions associated with desflurane stem from both its use and the remaining exhaled gases that contribute to atmospheric pollution. By analyzing standard procedures, hospitals can better understand their carbon footprints and alter practices, such as minimizing fresh gas flow, which significantly reduces the environmental impact of anesthetics.
Future Predictions: A Greener Healthcare System
As the NHS commits to a net-zero target, the medical field must seek innovative solutions to minimize the environmental impact of its practices. The concerted shift away from desflurane signals a future where anesthesiology can evolve sustainably. To maximize their impact, stakeholders must continue to collaborate and prioritize research into low-impact anesthetic alternatives and eco-friendly practices.
Why This Matters: The Human Connection
The implications of these practices extend beyond statistics; they reflect a profound commitment to patient safety and ecological preservation. By reducing anesthesia emissions, the healthcare community is not only enhancing patient outcomes but also acting as stewards for the planet, ensuring a healthier environment for future generations.
As we move forward, it is crucial for hospital administrators and medical professionals to champion environmentally-conscious practices. They hold the power to influence lasting change that can resonate throughout the healthcare system and beyond.
Take Action Now
The challenge to combat the climate crisis is monumental, but through these educational efforts and structural changes, the healthcare sector can make a significant impact. Explore how your institution can implement sustainable anesthesia practices to contribute to this vital cause. Join the movement for a greener, healthier future today!
 Add Row
Add Row  Add
Add 



Write A Comment