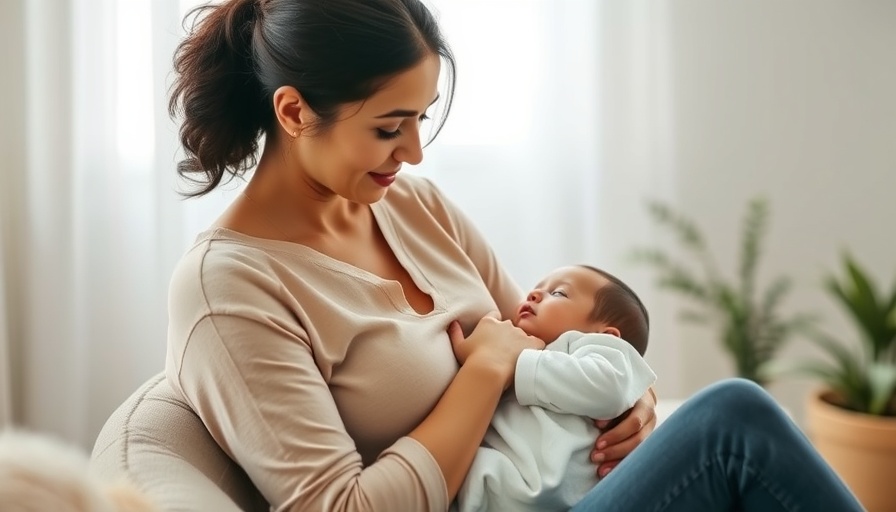

The Findings of the Recent Study
A recent study has cast doubt on the effectiveness of antenatal care contacts beyond the 4 to 7-year mark in promoting immediate and exclusive breastfeeding rates among new mothers. This crucial period is often regarded as pivotal for establishing healthy breastfeeding habits, yet the study suggests that extended antenatal care does not yield the expected benefits.
Understanding Breastfeeding Trends
Breastfeeding is vital for the health of both mothers and infants, providing essential nutrients and boosting immunity. Organizations like the World Health Organization advocate for exclusive breastfeeding for the first six months of an infant's life. However, the challenge remains in ensuring that mothers are effectively supported during this period. The study suggests that instead of focusing on prolonged antenatal sessions, health practitioners might need to rethink their strategies to enhance breastfeeding rates.
The Importance of Targeted Antenatal Education
Education is the cornerstone of successful breastfeeding practices, but not all educational interventions are equal. The findings indicate that instead of merely extending antenatal care contacts, healthcare providers should concentrate on the quality and relevance of the information provided during these sessions. Simplifying the communication of breastfeeding benefits, as well as inclining towards practical demonstrations in hospital settings, could help make a more substantial impact.
Global Perspectives on Breastfeeding Initiatives
Looking at global trends, several regions have adopted various approaches to improve breastfeeding rates. For instance, countries such as Norway and Sweden have implemented comprehensive support systems for new mothers that include home visits and targeted breastfeeding education during infancy, demonstrating that localized, culturally sensitive approaches may yield better results.
Future Predictions for Antenatal Care Practices
As we evolve towards a health landscape increasingly influenced by data and technology, future antenatal care practices might integrate digital health solutions such as mobile apps that provide tailored breastfeeding tips and real-time support. These innovative tools could complement traditional methods and allow healthcare providers to offer customized advice based on the mother’s individual needs and experiences.
Conclusion: Rethinking Our Approach to Antenatal Care
The study emphasizes the necessity of reassessing traditional strategies in antenatal care focused on breastfeeding promotion. By tailoring education and support to immediate needs rather than extending support over years, health professionals may enhance breastfeeding rates significantly. As the global health community continues to strive for better maternal and child health outcomes, understanding and adapting to new findings will be essential.
 Add Row
Add Row  Add
Add 



Write A Comment